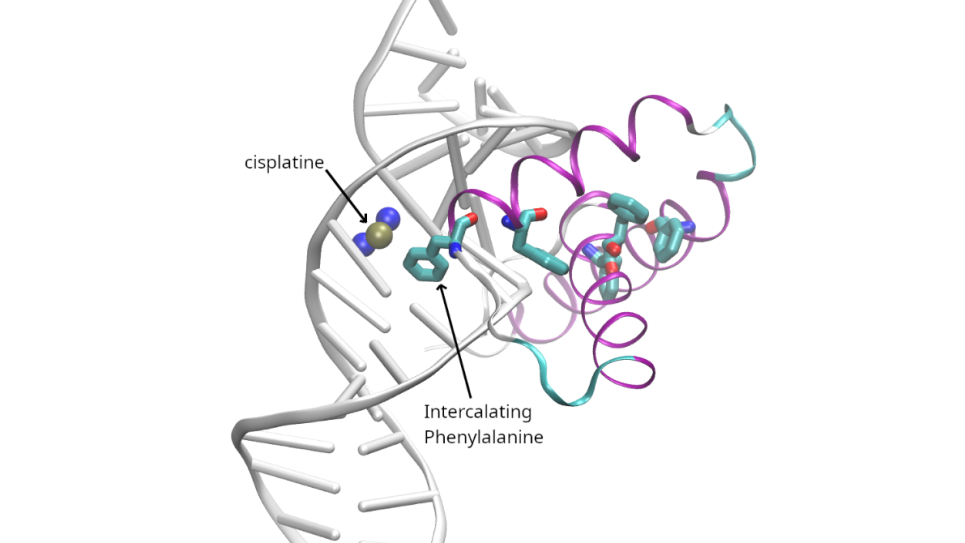
Cisplatin bending DNA by forming covalent bonds between its central platinum atom and two adjacent guanine bases, disrupting the DNA structure. The intercalating phenylalanine stabilizes the distorted DNA by stacking between the DNA bases, contributing to the overall structural deformation. Image: Anouar Benali, Qubit Pharmaceuticals


